STEAM teaching integrates cross-field aesthetics—Tumble Wooden Doll
Professor Zhang Yushan, Department of Science and Technology Application and Human Resources Development, National Taiwan Normal University
Xue Yayun, a graduate student in the Department of Science and Technology Application and Human Resources Development, National Taiwan Normal University
1. Foreword: The concept of STEAM education
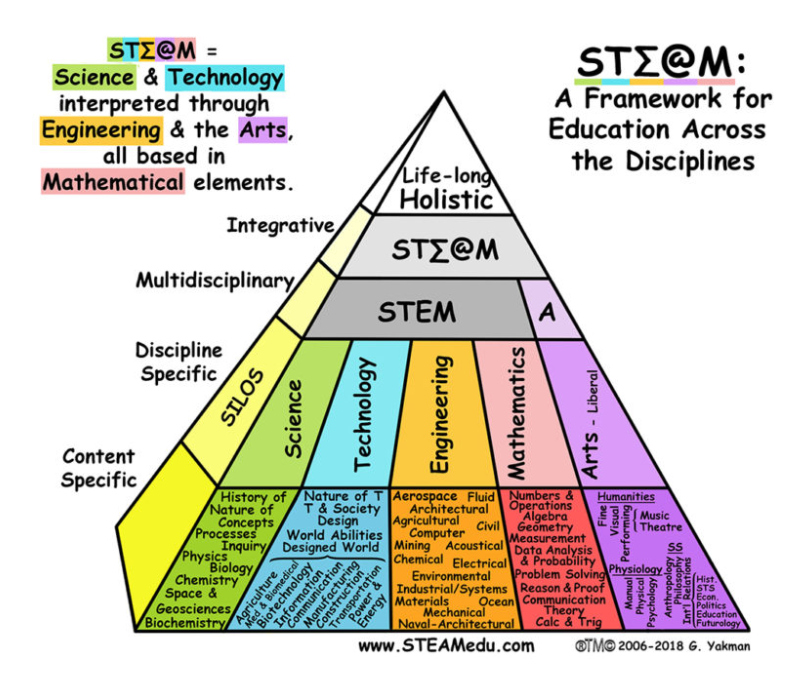
As early as 2001, the National Science Foundation (NSF) proposed the concept of SMET, emphasizing the importance of science, technology and education, which also implies the space war between the United States and the Soviet Union in 1957 (Lathan, 2021). Later, due to the shortage of scientific and technological talents, the United States vigorously promoted STEM education, especially the Obama administration (The White House, 2016). During this period, some scholars proposed the integration of ARTs (arts and crafts, language, sports, society), which became the first version of the STEAM Pyramid (Pedagogy Pyramid). It was continuously improved and updated to become the current version, which is also widely cited.
In the past, due to factors such as subject-specific education and entrance examinations, the knowledge fragments in the textbooks were incomplete and students' learning motivation was poor. Therefore, the integration of cross-subject and cross-domain learning and the literacy orientation that emphasizes the combination of context and context have been continuously emphasized. For example, the hands-on Maker movement has also been introduced into school curricula in various countries. Performance-Based Instruction, which emphasizes hands-on experiments and inquiry, is also highly valued in Taiwan (National Institute of Education, 2000).
According to the EU STEAM Teachers College, Australia's Brocklesby Public School, the University of Connecticut in the United States, the New Zealand Ministry of Education's Digital Learning Community (Te Kete Ipurangi, TKI) (2021), Canada's University of Calgary (University of Calgary, 2021), etc. According to the definition, STEAM is an educational method that guides students to use STEAM to explore, integrate, and think critically (Te Kete Ipurangi, 2021; University of Calgary, 2021). In line with the core competencies and literacy-oriented concepts of the new curriculum, STEAM is an educational method that guides students to use STEAM to experience exploration, design thinking, and creative innovation. The output of STEAM is learning ability, cross-domain ability, practical ability, and creativity (Zhang Yushan, 2019; 2020).
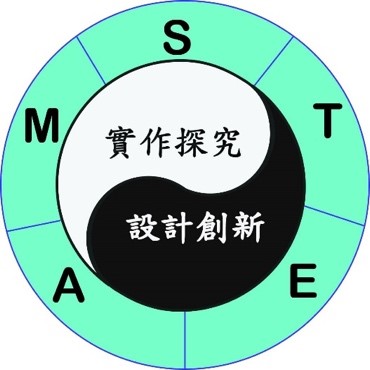
The core value of STEAM education lies in practical inquiry and design innovation, emphasizing the connection with the real world, starting from life and applying it to life (Zhang Yushan, 2019; 2020). In life situations, teachers guide students to discover problems through design thinking, use technology to solve problems, and also realize the significance and value of subject knowledge in various fields. Similarly, in life situations, teachers guide students to explore external knowledge and scientific principles through practical experience. These knowledge and principles can also be transformed into the basis of new scientific and technological innovations. Therefore, STEAM education emphasizes the combination of teaching themes and life situations. Through thinking, inquiry, practice and innovation, knowledge, abilities and attitudes are integrated and applied in the contextualized learning process, so that practical inquiry and design innovation can complement each other. , the concept of the taiji ("Supreme Ultimate") appears in both Taoist and Confucian philosophy, and represents the fusion or mother of yin and yang into a single ultimate, based on the dynamic relationship between Yin and Yang ) (Wikipedia, 2021; Zhang Yushan, 2021), as shown in Figure 2.
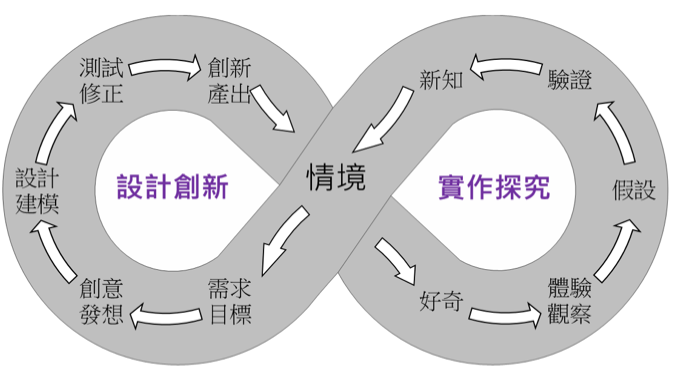
Ideal STEAM teaching must integrate practical inquiry and design innovation. The scientific inquiry model includes POE model (predict, observe, explain), POEC model (predict, observe, explain, compare), 4E (participate, explore, explain, evaluate), 5E (participate, explore, explain, refine, evaluate) ), 6E (engage, explore, explain, implement, deepen, and evaluate) (Burke, 2014; Barry, 2014), and even 6E+ (Engage, Explore, Explain, Engineer, Enrich & Innovate, Evaluate & Integrate) (Zhang Yushan, Weng Zihan, 2021; Cingil Barış, 2021; Sutiani, Situmorang, & Silalahi, 2021). Design thinking is a task-oriented problem-solving method, including the five-step design thinking proposed by the Stanford University School of Design (Empathy, Define the problem, Ideate, Model Prototype, and Test), or 4D Design pattern (discover, define, develop, deliver) (Silva & Blessing, 2021). Combining scientific inquiry procedures and design thinking procedures, a design inquiry cycle is obtained. STEAM education is based on life situations, allowing students to integrate knowledge and skills to deal with real-world problems, including creative ideas, test corrections, experiential observations and hypothesis verification, etc., and these steps and methods are in an infinite loop, Continuously adding elements of innovation and critical thinking not only increases the breadth, accuracy and diversity of students' knowledge application, but also provides a logical thinking structure that is consistent with reality, emphasizing the application of knowledge and the integration of learning and application, as shown in Figure 3.
2. Instructional design
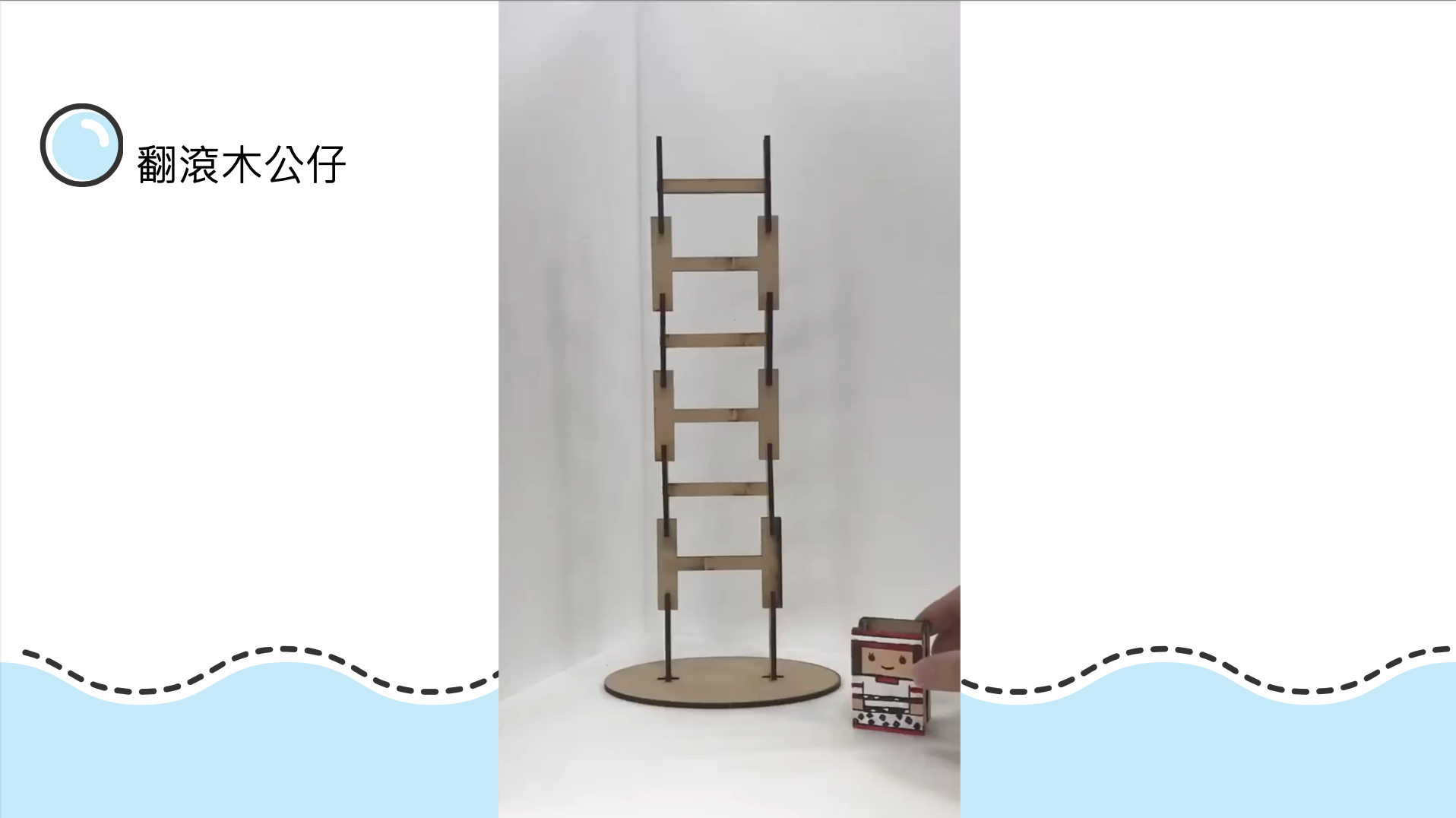
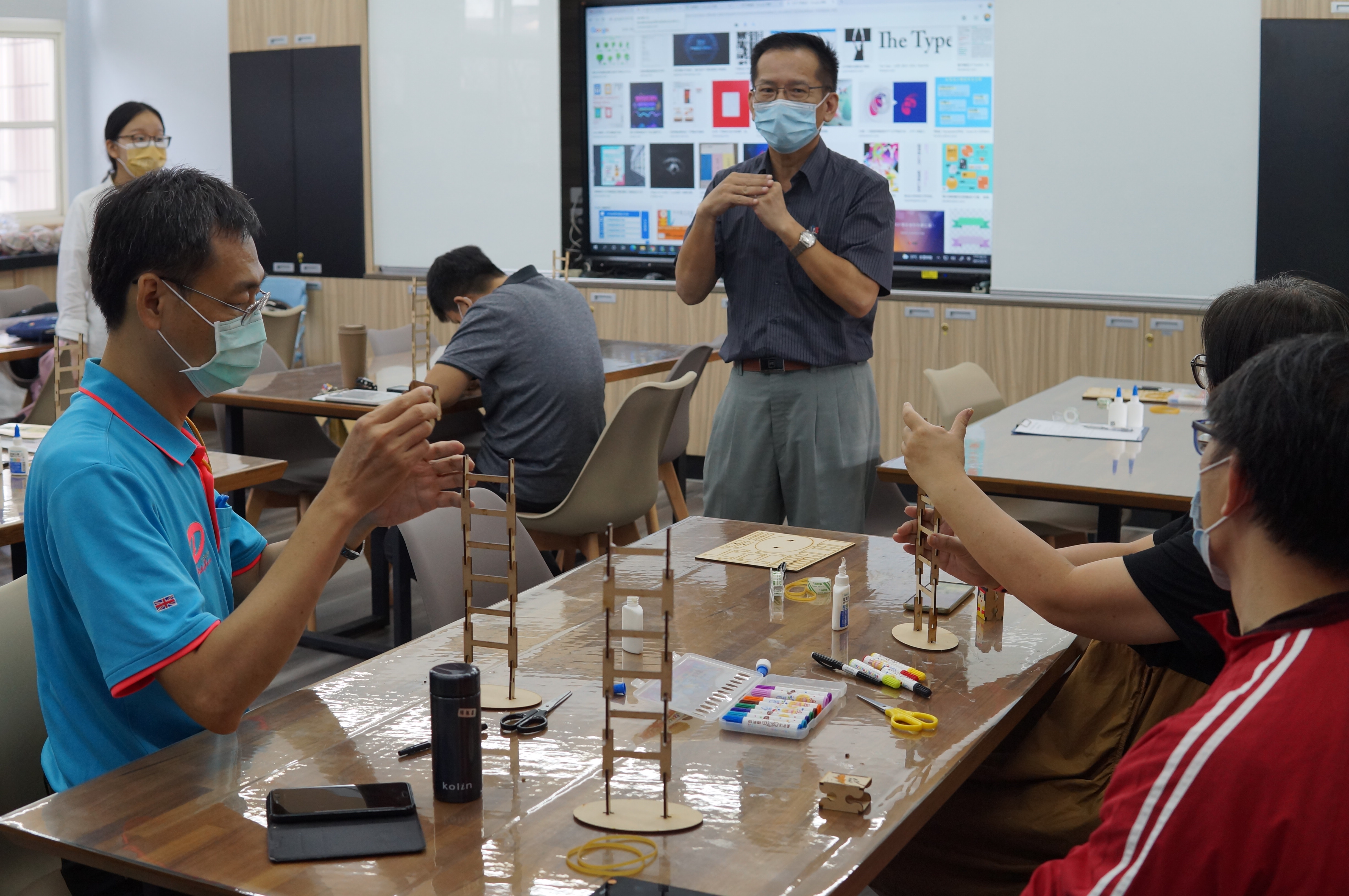
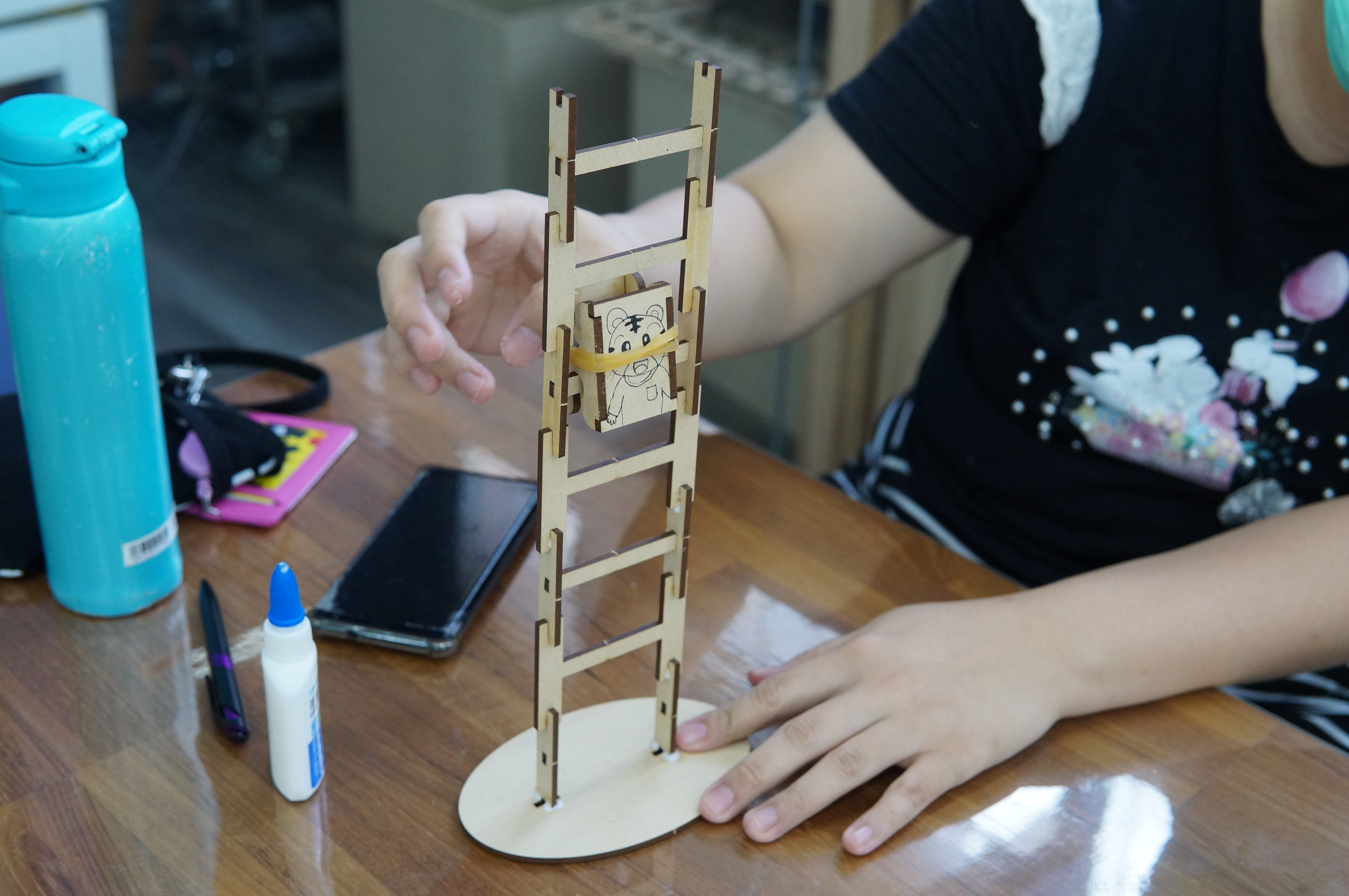
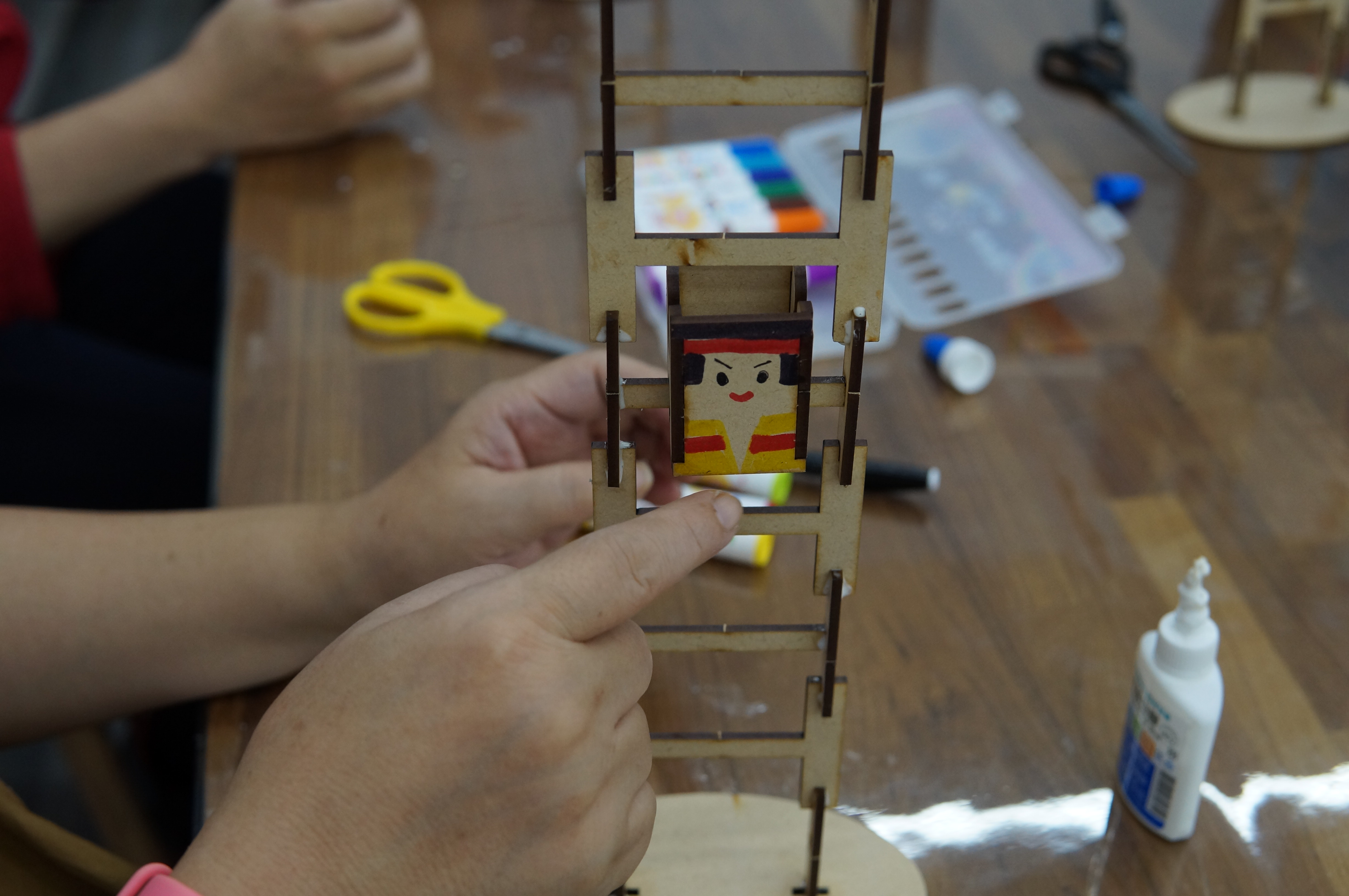
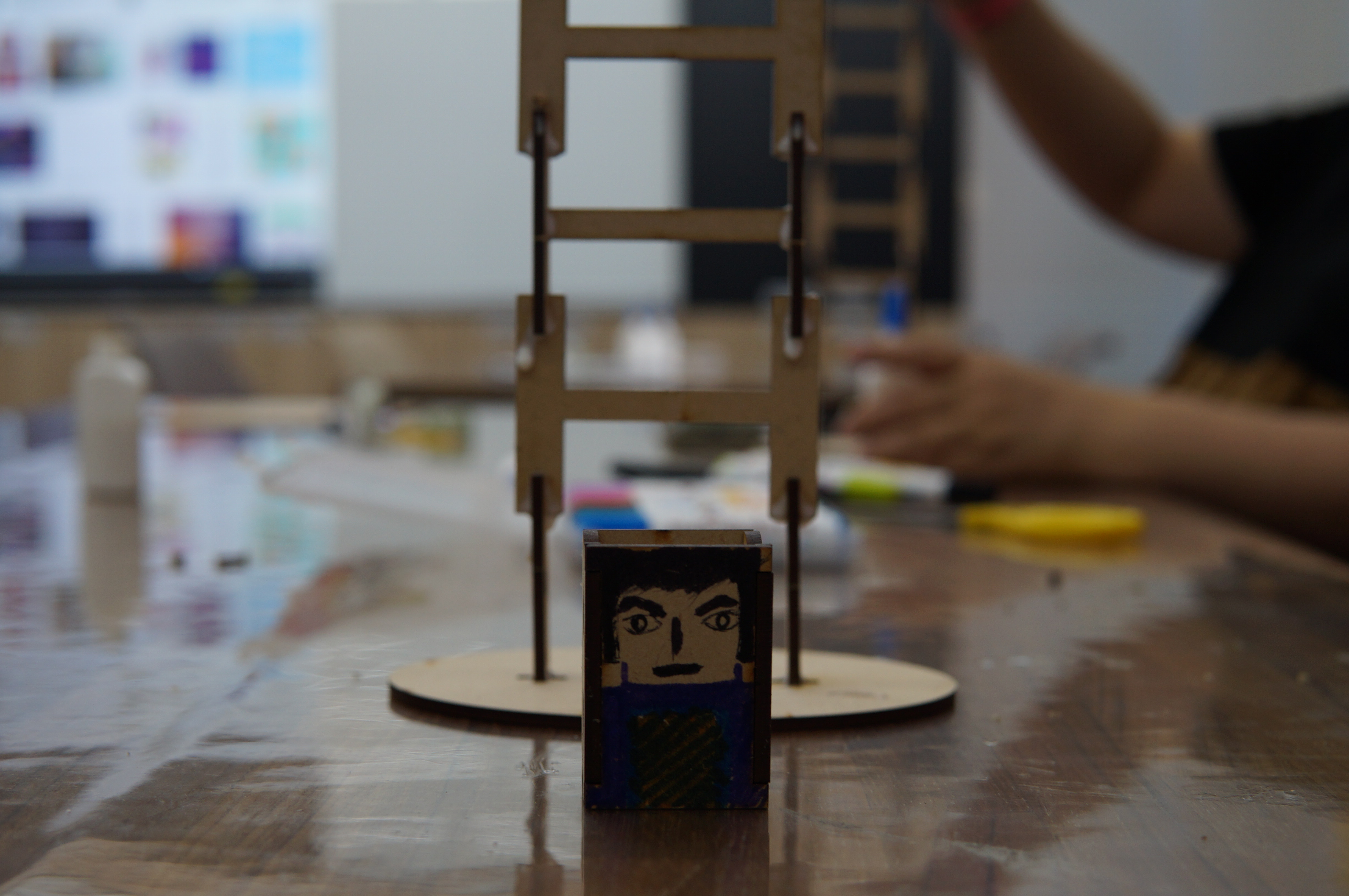
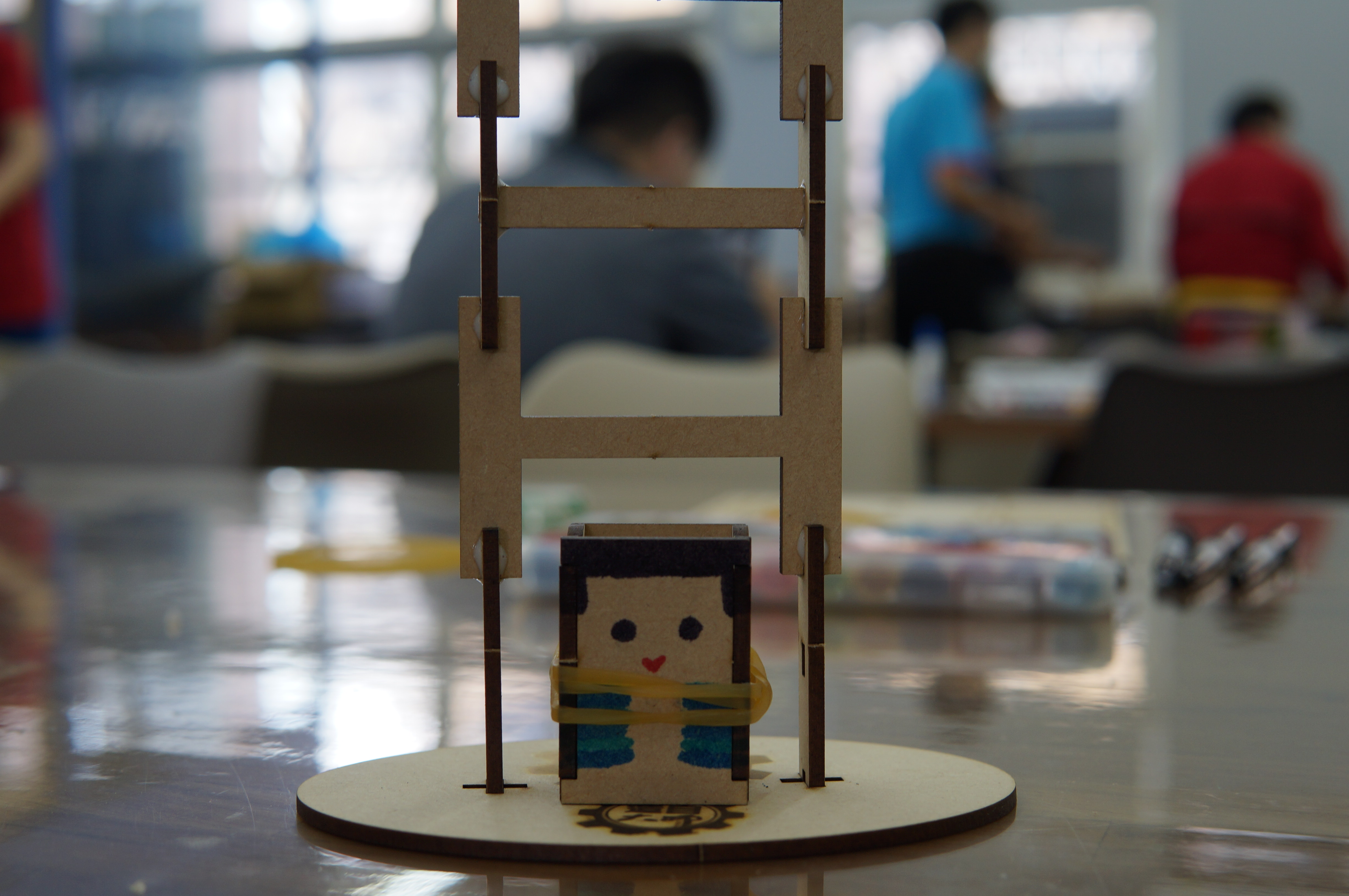
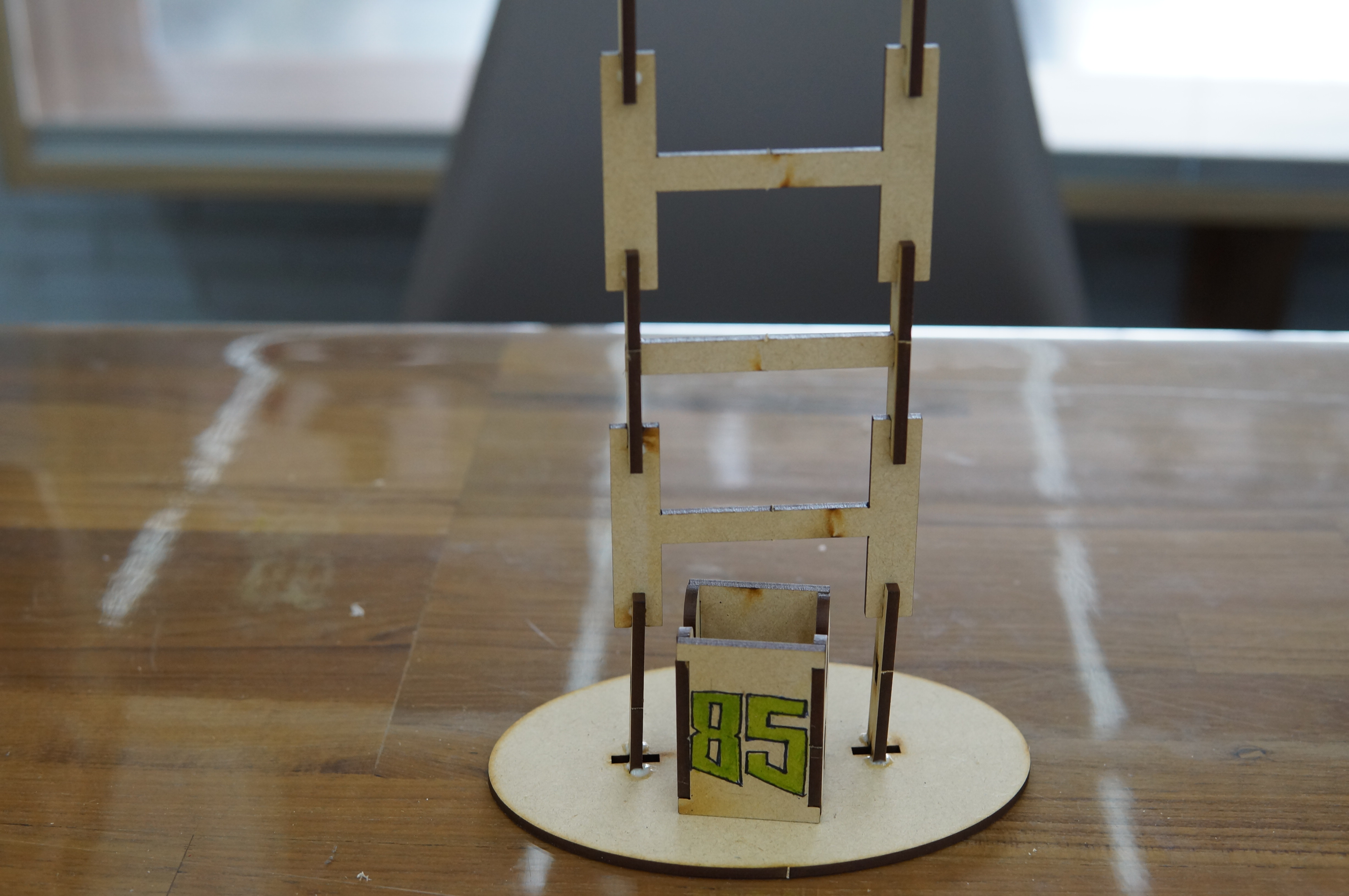
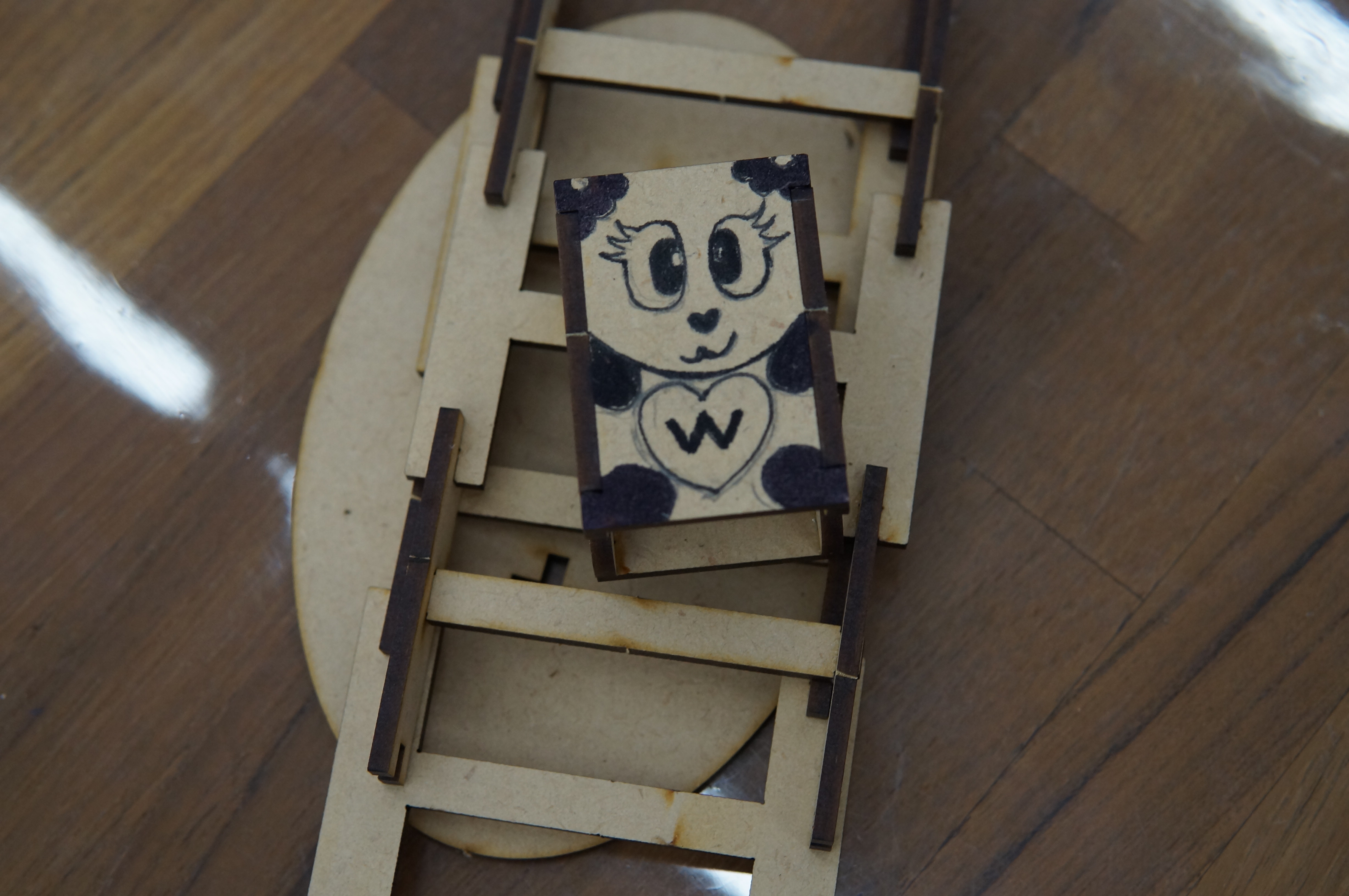
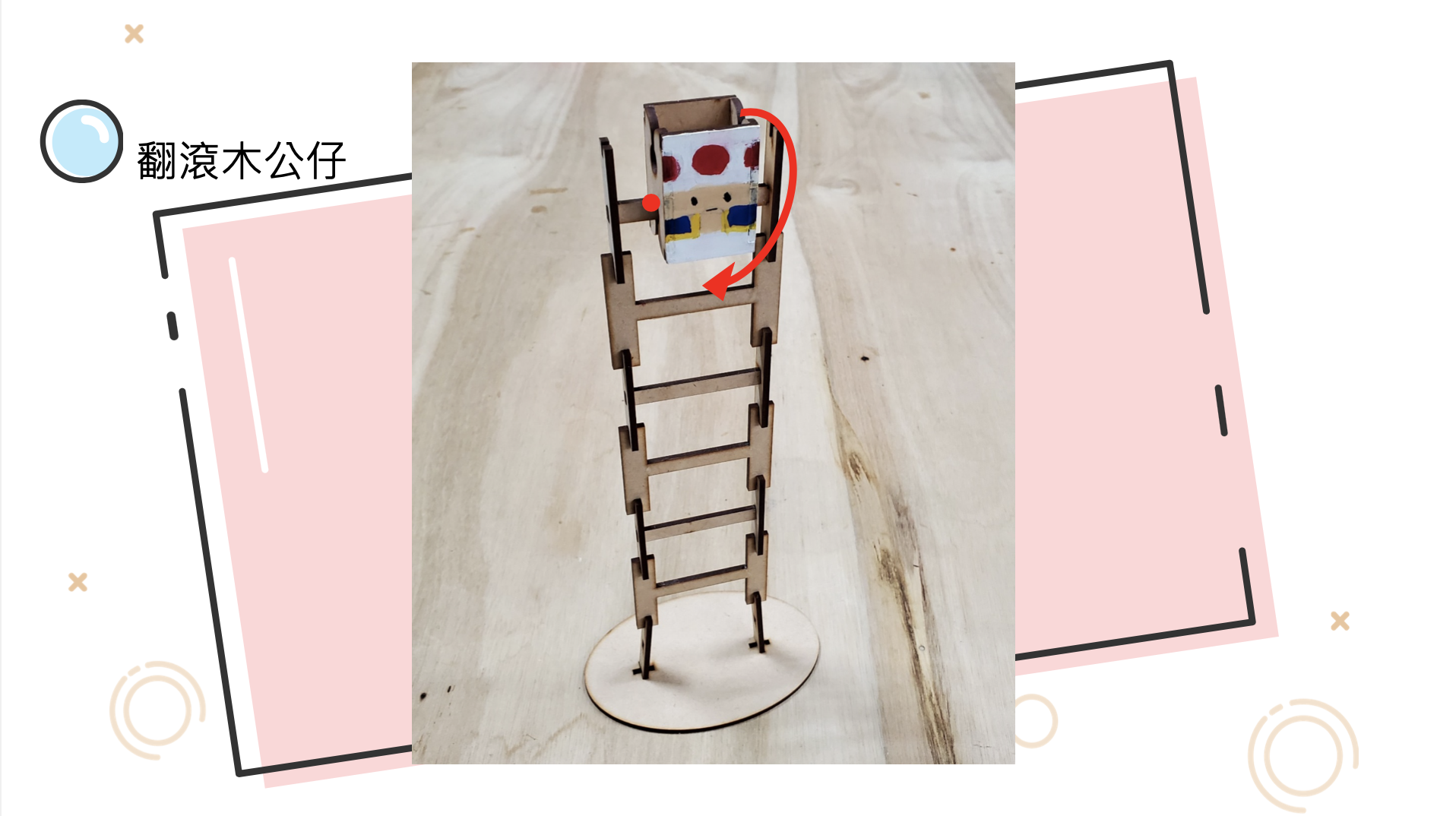
The theme of this teacher training is "Tumbling Wooden Dolls", which mainly emphasizes the integration of knowledge between disciplines and uses STEAM education to horizontally connect science, technology, art, humanities and other fields. The tumbling wooden doll combines the two scientific principles of leverage and gravity. Through the change of the center of gravity and the fulcrum, a moment of inertia is generated, making the wooden doll appear unbalanced. It rolls down from the ladder step by step. Through hands-on experience, Cultivate the habit of using both hands and brain, and the integration of cross-domain aesthetics further activates the integration with other disciplines and enhances the performance of cross-domain learning.
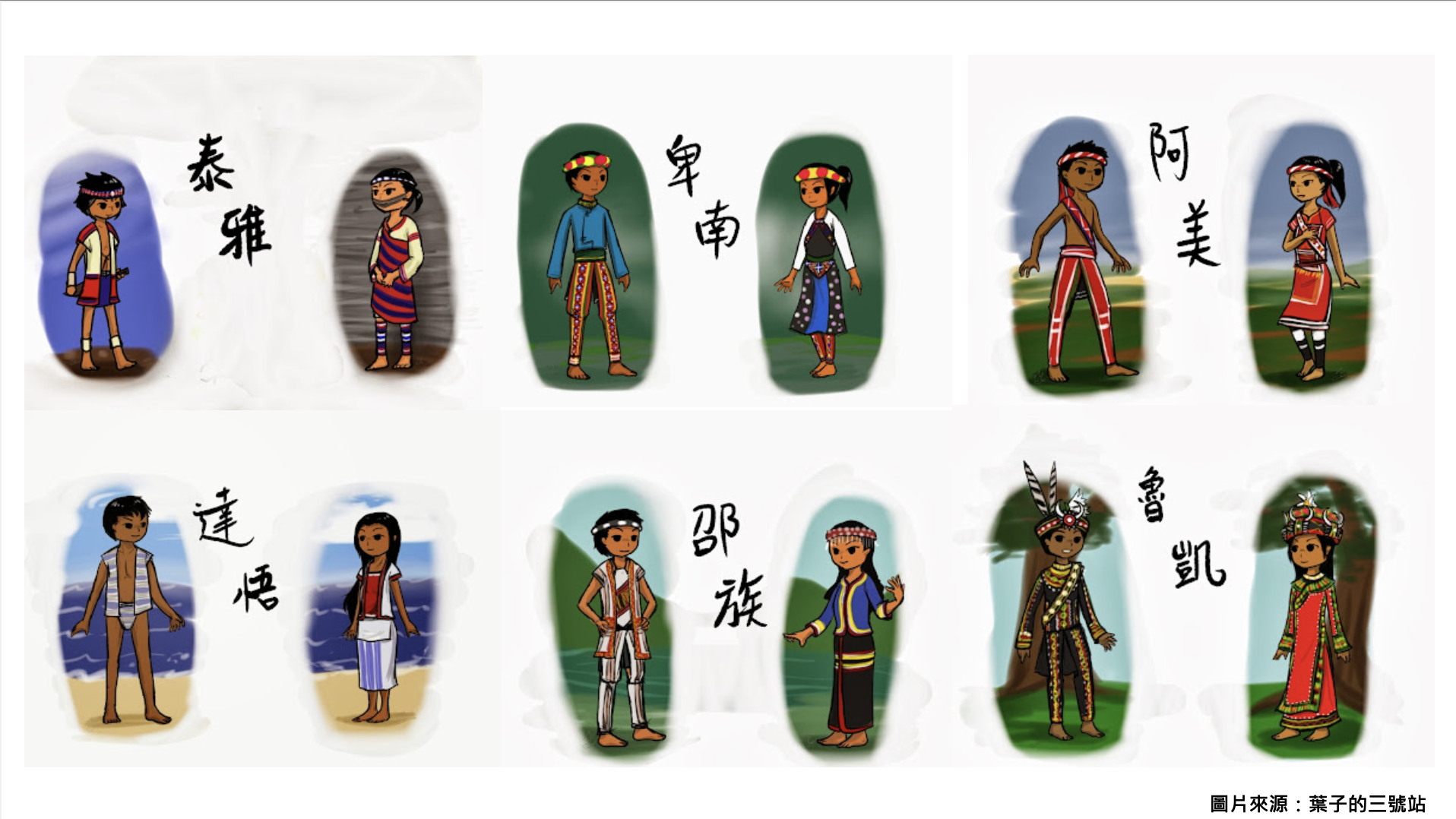
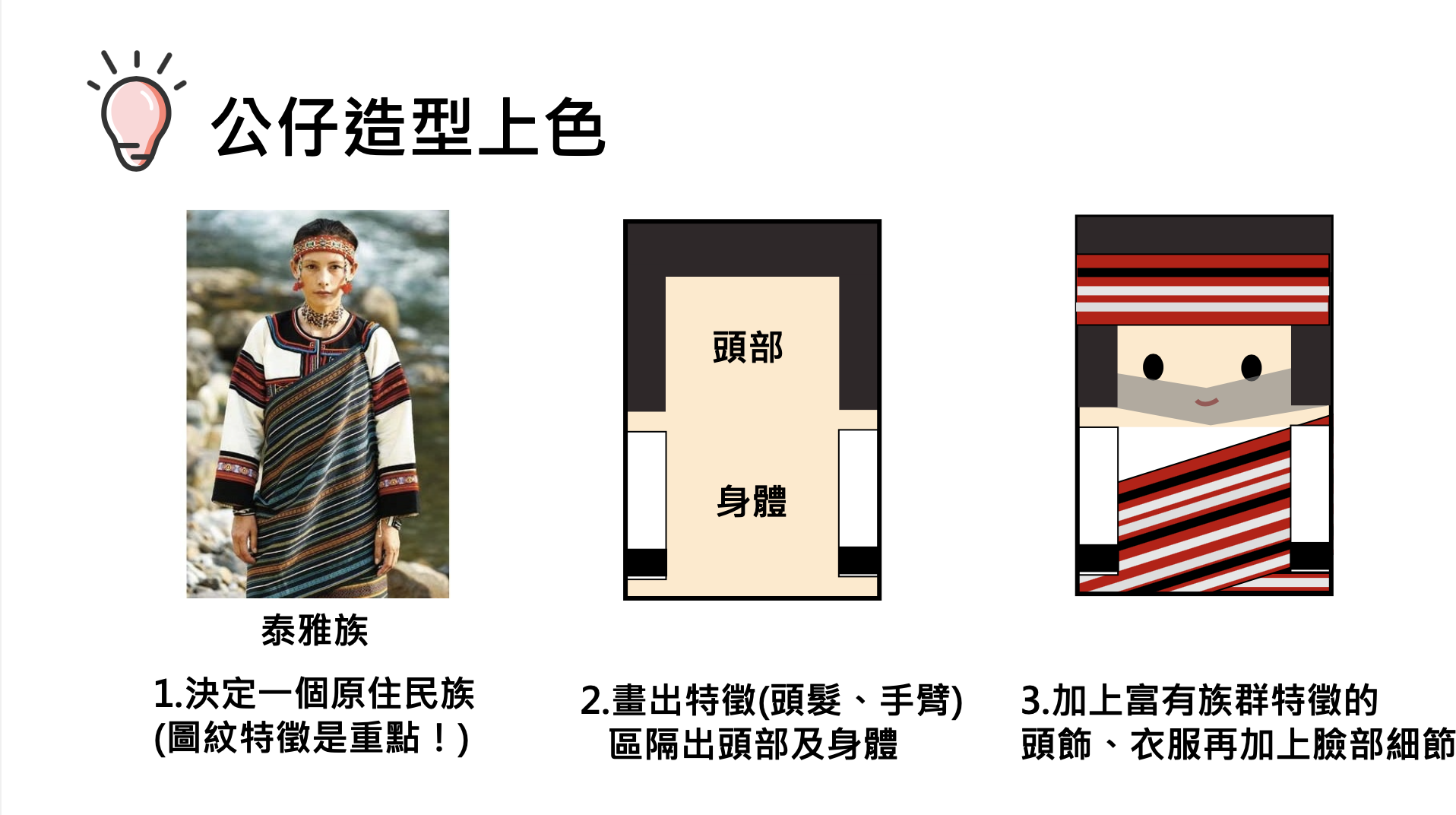
The object of this activity is to study with teachers from an elementary school in Taipei City. Before the course begins, the teaching aids are displayed, and visual stimulation is used to guide the teachers to figure out what causes the wooden dolls to roll. The practical part is integrated into cross-disciplinary aesthetic teaching, combined with The issue of education of indigenous peoples is integrated with primary school social field courses by introducing the unique culture and costumes of indigenous peoples.
(1) Twelve-year national education curriculum - key points in the field of science and technology
The 12-year National Basic Education course in the field of science and technology aims to cultivate students' abilities to "do, use and think" so as to possess the technological literacy required in the 21st century. In order to be able to apply what they have learned when facing current life and future challenges. Cognition, emotion, and skills are applied in life situations and by integrating theory and practice to solve problems and meet needs.
The learning focus in the field of science and technology is mainly composed of "learning performance" and "learning content". Learning performance includes the two structures of computational thinking and design thinking, which refers to students' specific performance of core competencies, including knowledge, skills, abilities and affection; The learning content is based on practical activities, guiding students to use design, production, analysis and integration, and properly use tools, equipment or materials to solve scientific and technological problems in daily life, thereby cultivating correct scientific and technological attitudes. In line with the rapid development of technology and information society, as well as the needs, problems and other challenges arising from changes in lifestyles, in addition to learning basic knowledge, students should also strengthen their hands-on practical and interdisciplinary integration abilities, and try to make use of relevant knowledge in various disciplines. knowledge to solve problems.
(2) STEAM education applied in this activity
STAEM cross-domain integrated teaching is an interdisciplinary integrated teaching method to make up for the problem that traditional teaching emphasizes theory and lacks practical connections. The Ministry of Education stated in the "Core Competencies" of the 12-year National Education Curriculum: "Competencies refer to the knowledge, skills and attitudes that people should possess when adapting to current life and facing future challenges." In emphasizing cross-domain integration and Under the literacy-oriented call for situational application, the importance of A (Arts) in STEAM is highlighted. Among them, "A" not only refers to art in a narrow sense, but also in a broad sense, integrating the art field and social and humanities disciplines. It is expected that learning, design and creation can have warmth and care, strengthen the effect of cross-domain integration and the connection with real life. sex.
(3) Cross-field aesthetic teaching integrated into this activity
According to the art field of the 12-year National Basic Education Curriculum, the core competencies in the art field emphasize that art learning is not limited to knowledge and skills, but also pays attention to the integration of art learning with life and culture, through "expression", "appreciation" and "practice" Aspects of learning, accumulating aesthetic experience, cultivating student-centered sensory perception, aesthetic thinking and creative expression abilities, and enriching artistic accomplishment and aesthetic literacy (Ministry of Education, 2018). Through cross-field aesthetic teaching with the art field as the core, aesthetic experience can enhance students' cognition and application ability of beauty through cross-field learning and practice (Yu Huirong, Zhao Huiling, Lin Xiaoyu, and Li Qichang, 2015).
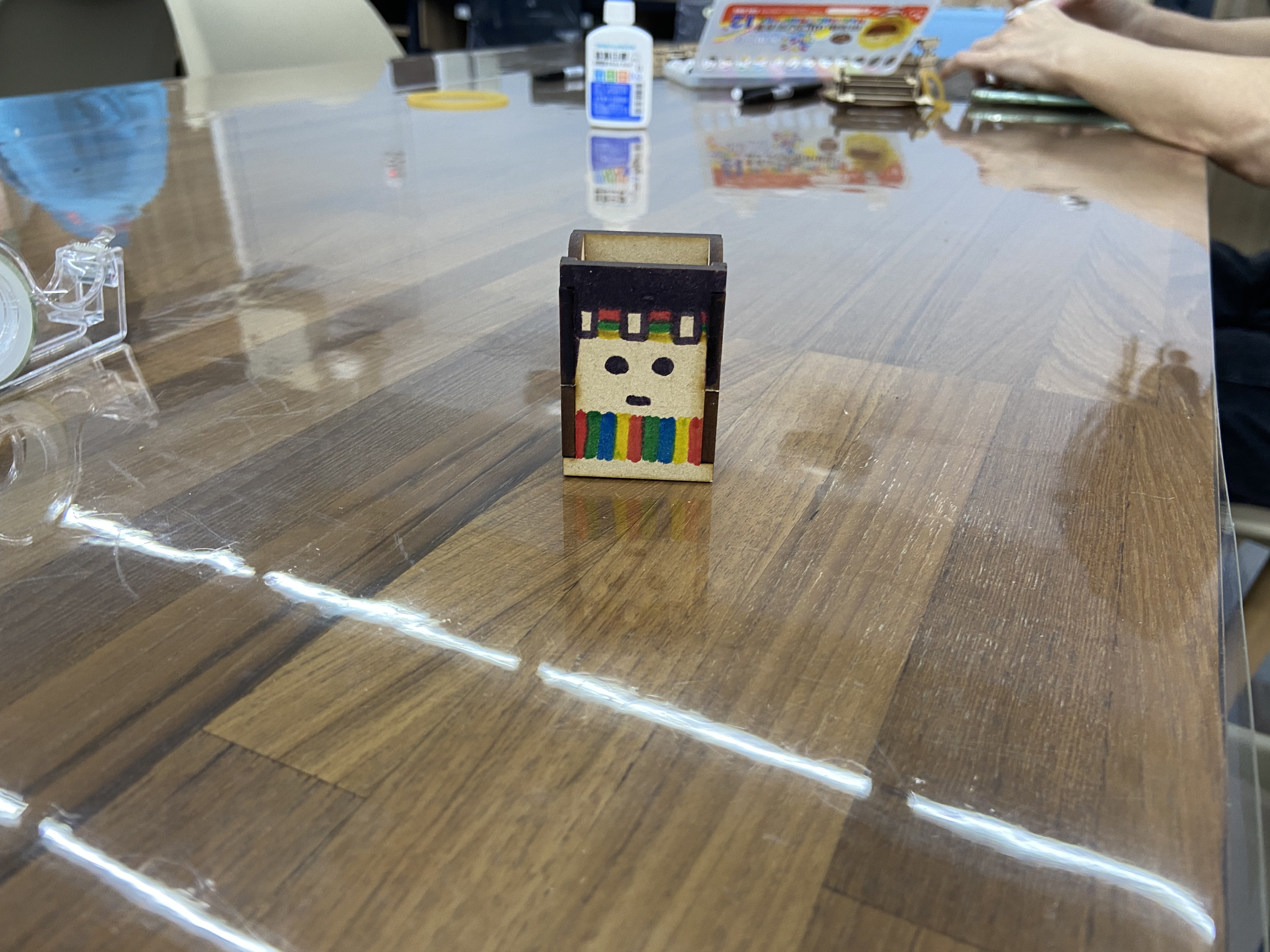
In addition to being presented in works of art, aesthetic experience also exists in daily life. Aesthetic education is not about learning skills or knowledge, but about inspiring our sensitivity to humanistic society and multiculturalism, including discovery, exploration, respect, acceptance, etc. course. Therefore, in order to transform the aesthetic experience into life, the cross-disciplinary aesthetic teaching of this activity combines Taiwan’s local aboriginal culture to introduce the rich cultural context of the aboriginal people and the clothing design containing unique aesthetics. It is also hoped that through the integration of the topic, In addition to contributing to aesthetic literacy, it also enhances the richness of cross-domain learning and regional care.
| learning aspects | activity procedure |
| Performance | Introduce the cultural characteristics of Taiwan's aboriginal people, and use the traditional costumes of the aboriginal people as the main theme to convey the differences in clothing design, color matching and decorative accessories of each ethnic group. |
| Appreciation | Understand the shapes, color expressions and totem images of various ethnic groups. |
| practice | Use different color combinations and color block combinations to plan and design to form a visual aesthetic. |
(4) Teaching activities of rolling wooden dolls
1. Teaching objects: The objects of this teaching activity are teachers from various fields in a public elementary school in Taipei City, a total of 12 teachers.
2. Teaching time: This activity is a training activity for teachers in the school. The training activity lasts for 1 hour.
3. Teaching activities
| Teaching activity content and implementation methods | time |
|
Cause motivation: This teaching activity "Tumbling Wooden Doll" is introduced. Through the display of teaching aids, teachers are guided to think about what causes the wooden doll to roll. |
5 |
|
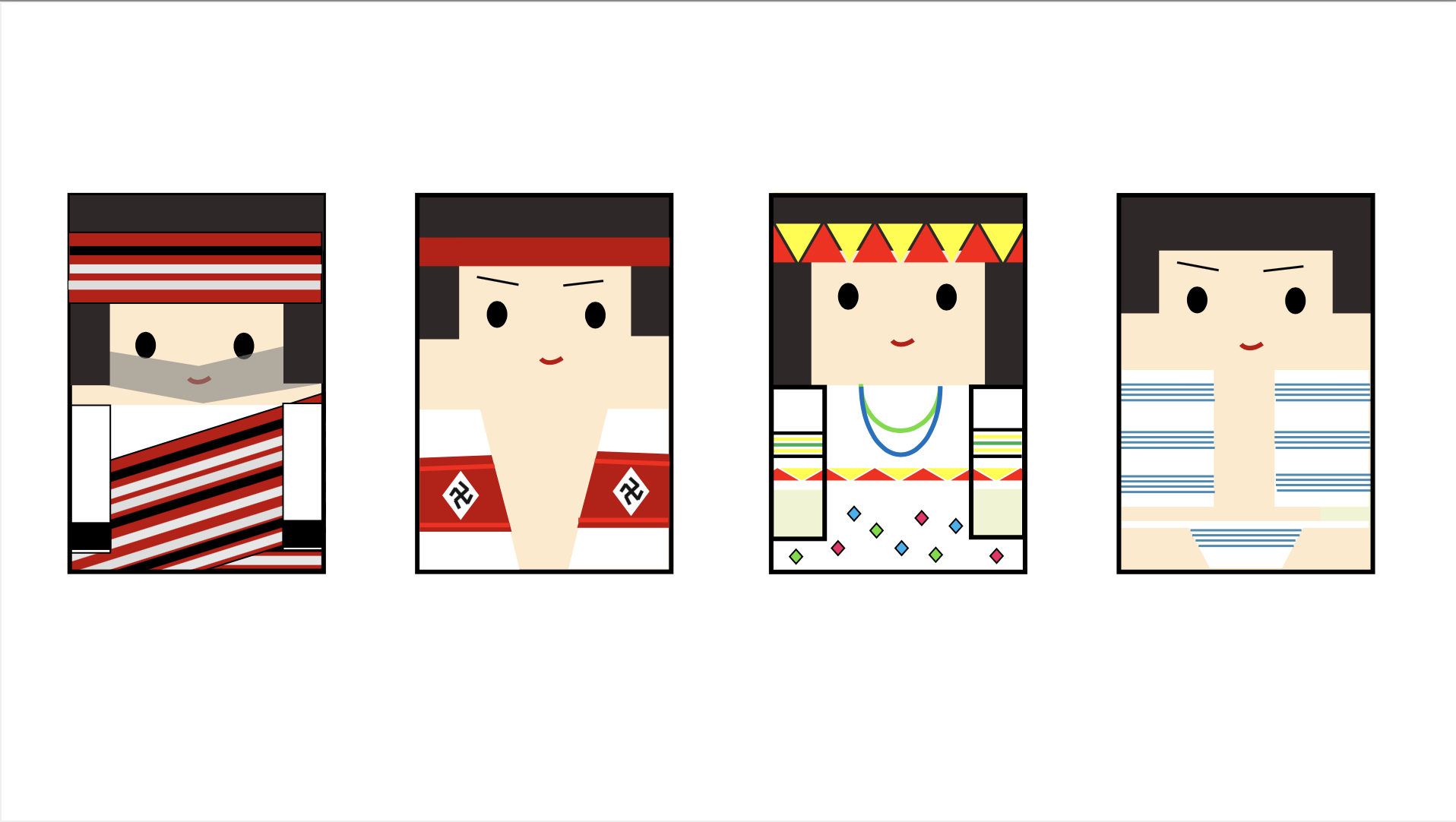
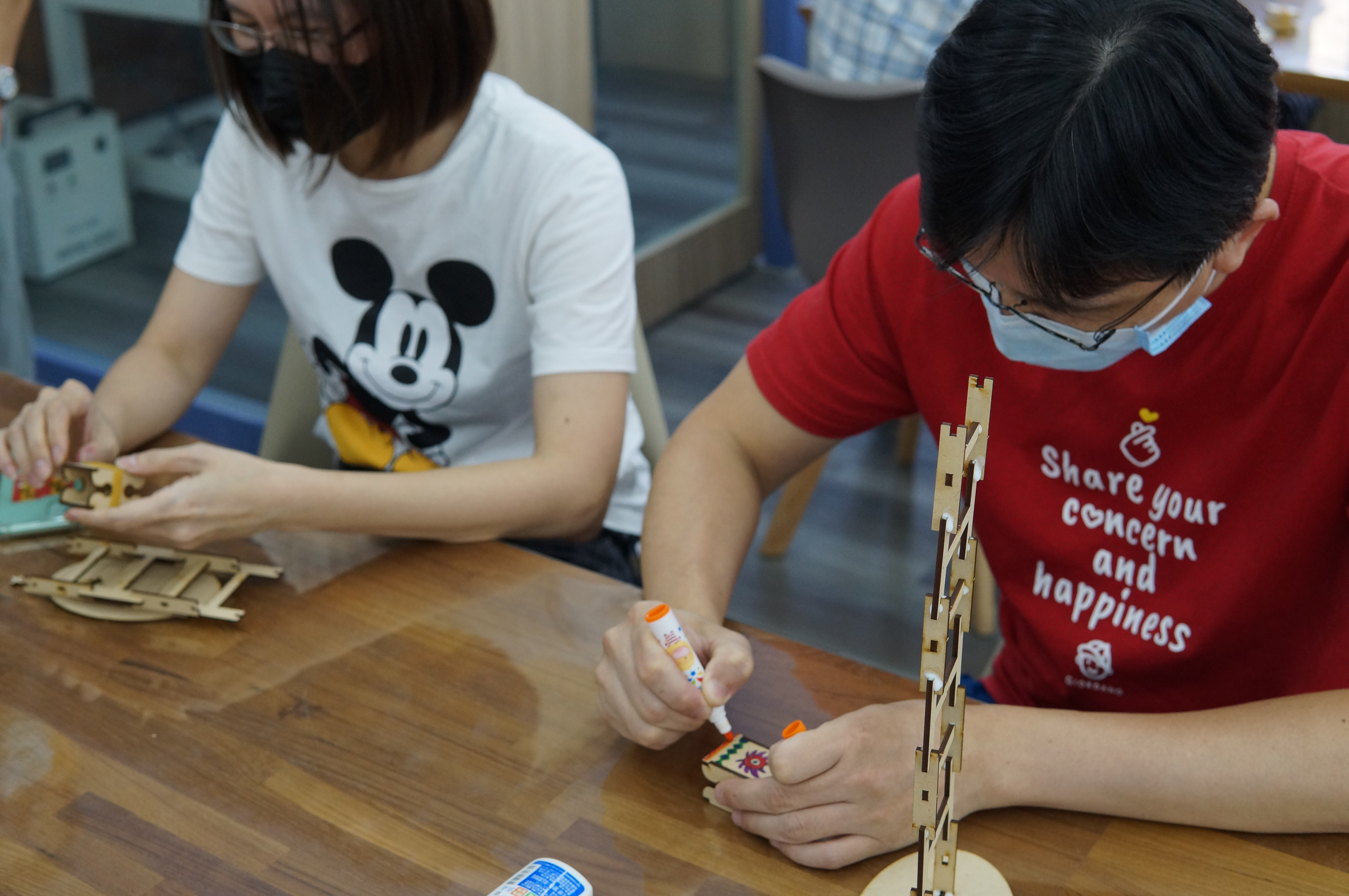
development activities 1. Introduce scientific principles (gravity, center of gravity and fulcrum) and connect life experience with examples (gravitational potential energy and moment of inertia), and provide teachers with additional teaching aids that explain other similar principles. 2. Introduce the number of Taiwan’s aboriginal ethnic groups, the date of the aboriginal ethnic groups, the differences in clothing between men and women of each ethnic group, colors and decorative accessories, and the unique traditional culture (such as face tattoos). 3. Introduce the doll coloring techniques. Based on the types of aboriginal clothing, woven patterns and clothing colors, adjust the color distribution ratio, simplify it and present it in the form of color blocks, and finally display the visual beauty through arrangement and combination. |
|
|
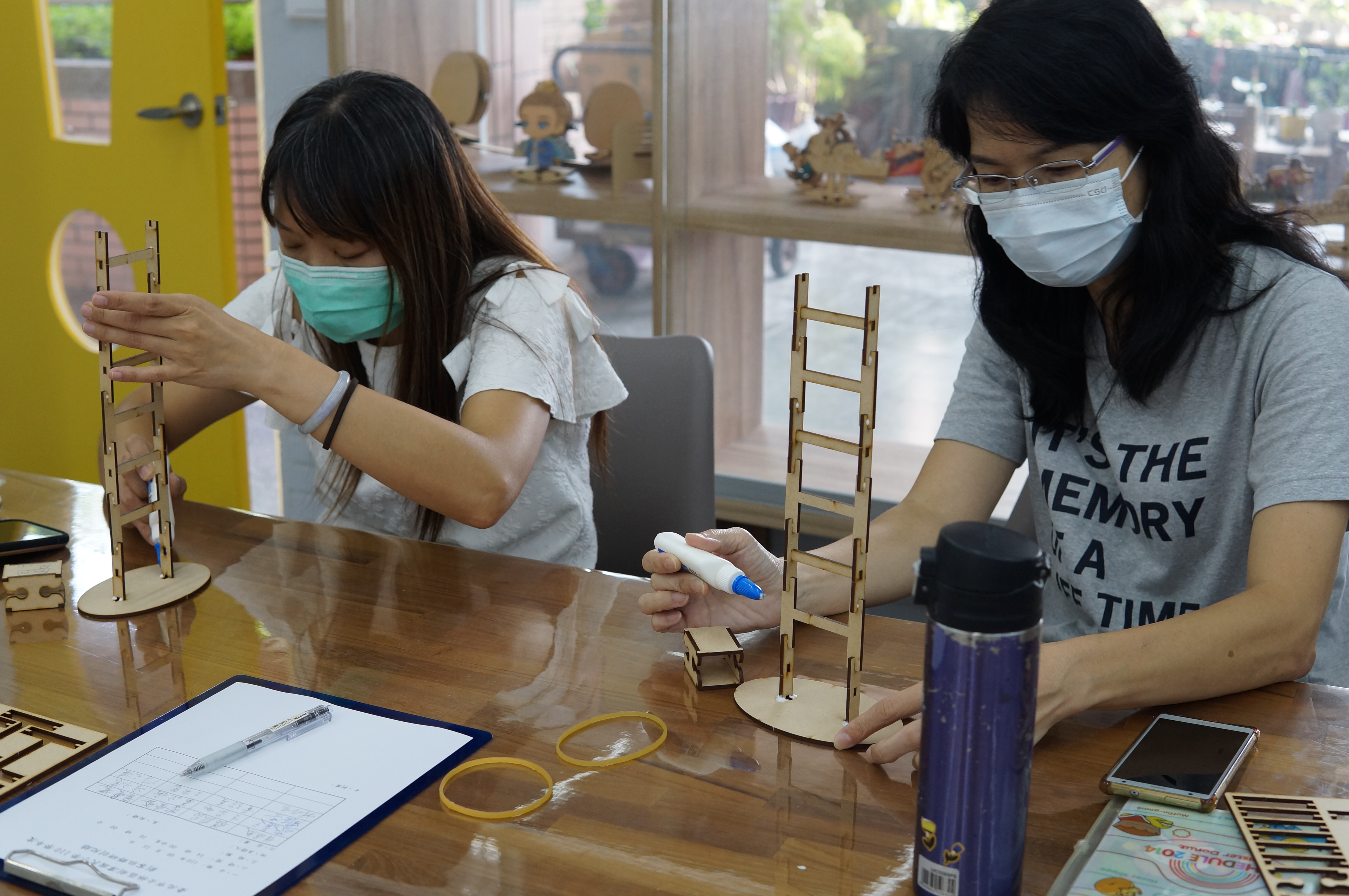
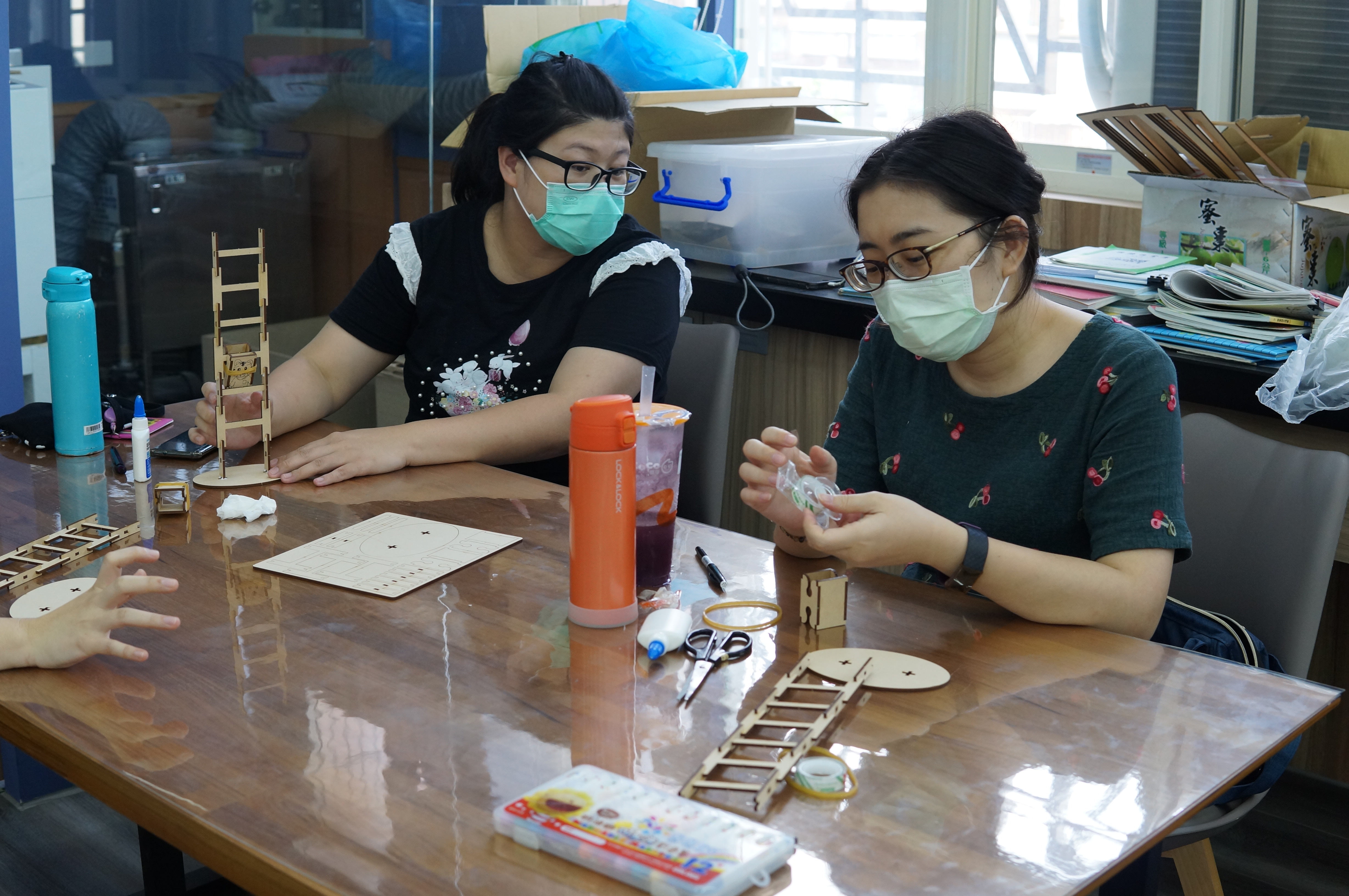
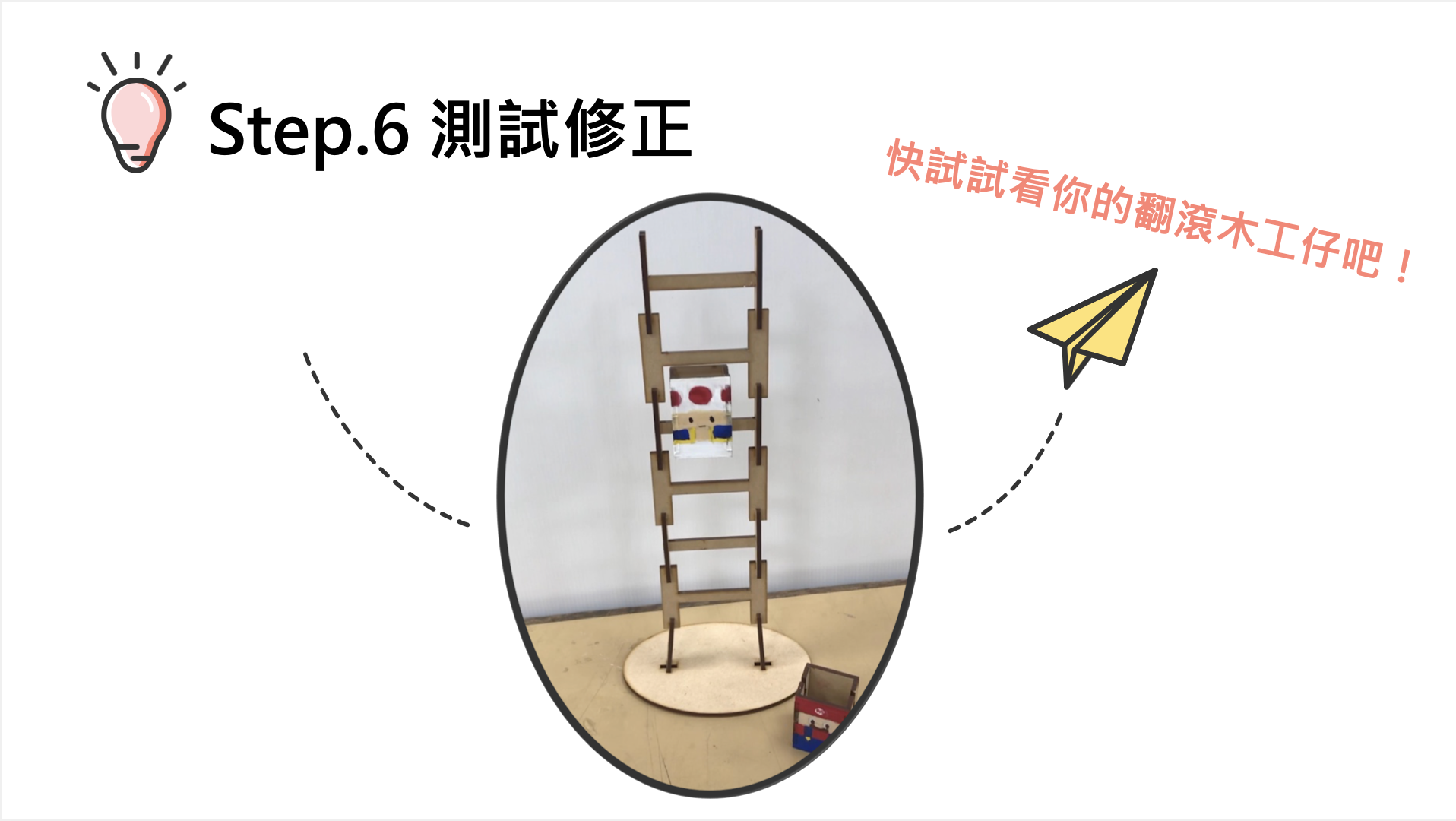
Implementation activities 1. Distribute materials and explain tool operation precautions. 2. Explain the production process (1) Assemble the doll (2) Test correction (3) Aesthetic design |
|
|
Summary activities This activity is based on the steps of experiential inquiry and design innovation, guiding teachers to arrange the steps in lesson plan design, and share four key questions, which can allow students to explore and think, apply them to their works, and further innovate or improve. 1. Basic principle: Why does the doll fall down? 2. Key factors: (1) What will happen if the doll is too big? (2) What will happen if the doll is too big? 3. Improvement and refinement: Regarding the shape or size of the side of the doll, what kind of design is better? |
3. Teaching reflections and suggestions
This article integrates cross-field aesthetics into STEAM education and combines the fields of art, humanities, science, society and other fields to design flipped wooden doll practical teaching and research activities. The main results and findings of the field teaching are as follows:
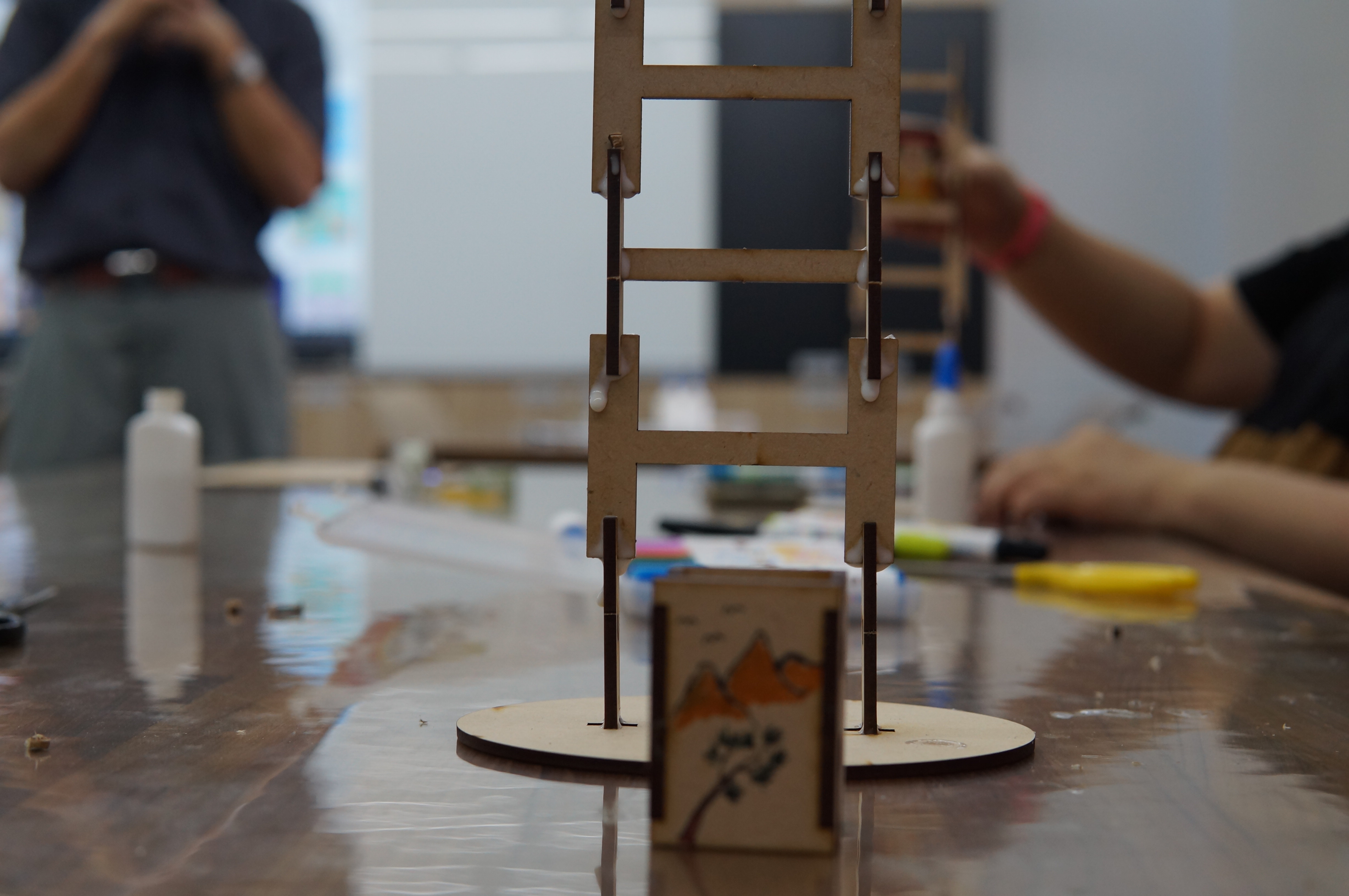
(1) Teachers are highly interested in experiencing the practice, have high willingness to participate, and are seriously committed. The assembly steps of the rolling wooden doll are relatively easy for teachers, and they can complete them quickly in a short period of time.
(2) Regarding the problem that the tumbling wooden doll cannot roll smoothly, the teacher will try to measure various possible factors through observation, analysis and judgment. If he still cannot succeed, he will ask other teachers and lecturers to understand the problem and Gain new experience from problem solving.
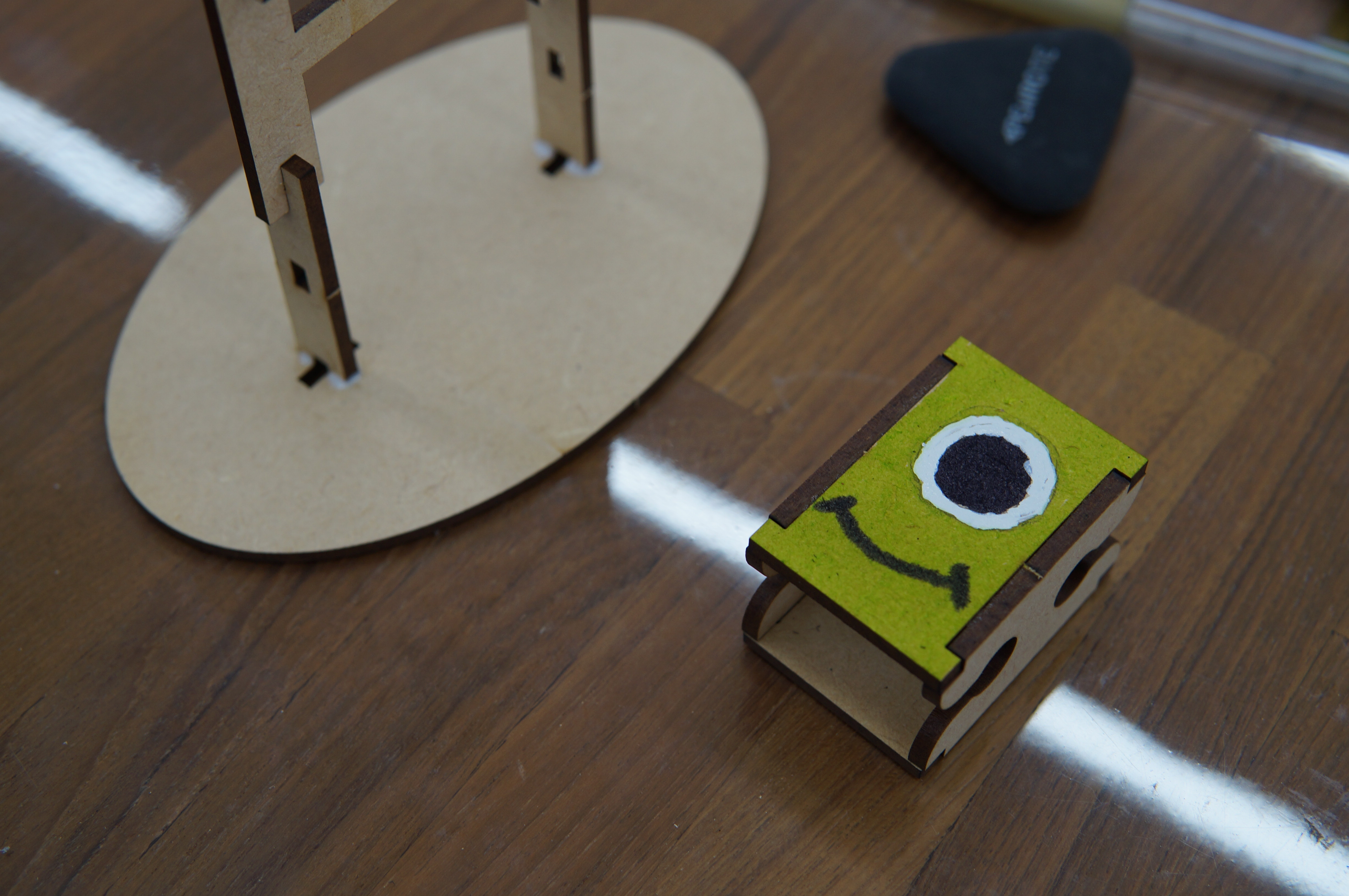
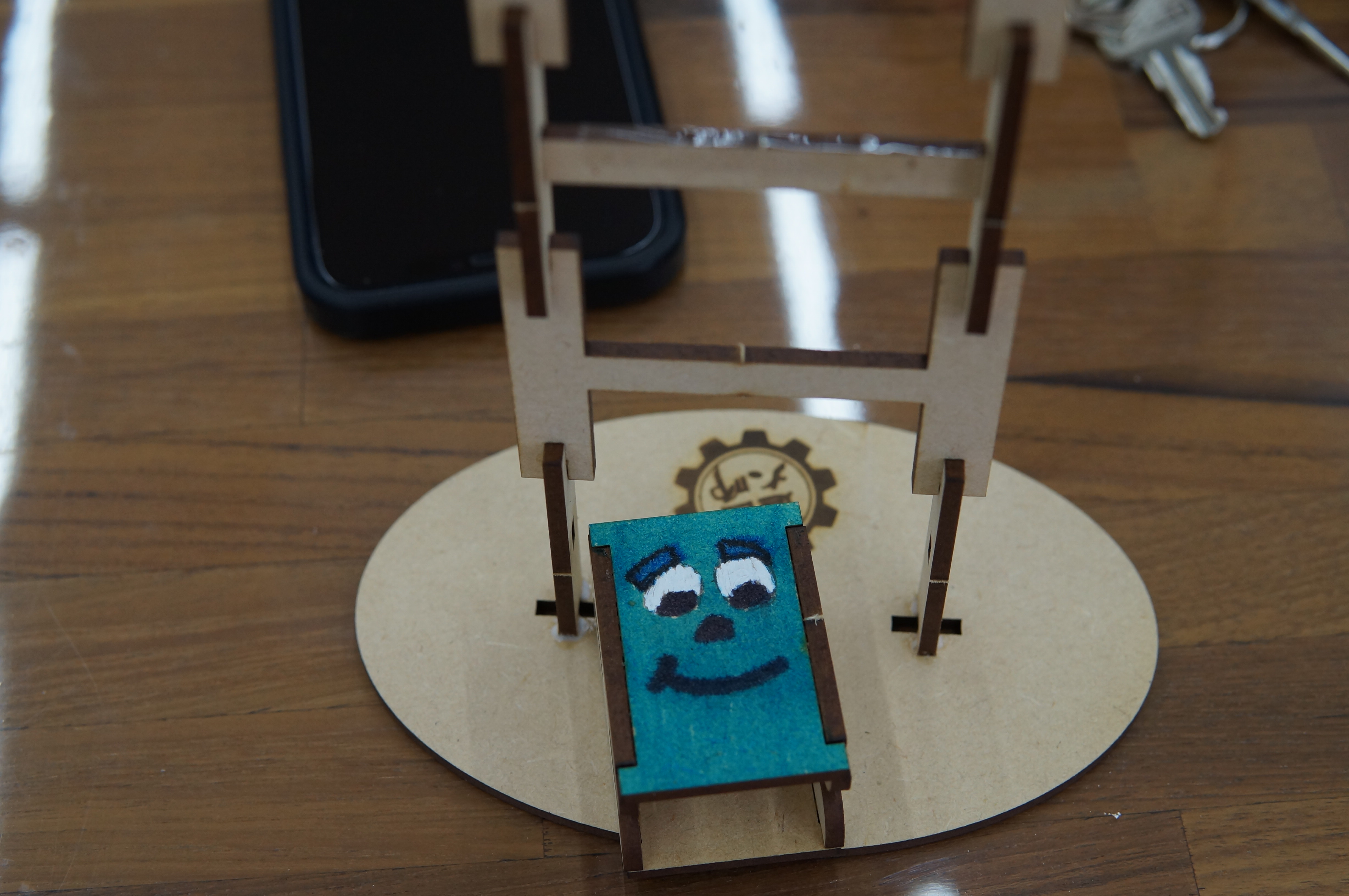
(3) Teachers have good performance in creative design. In addition to using aboriginal costumes as the main theme of aesthetic design, some teachers also extended the theme to other theme style designs, such as sports and art, to achieve the effect of cross-domain integration. .
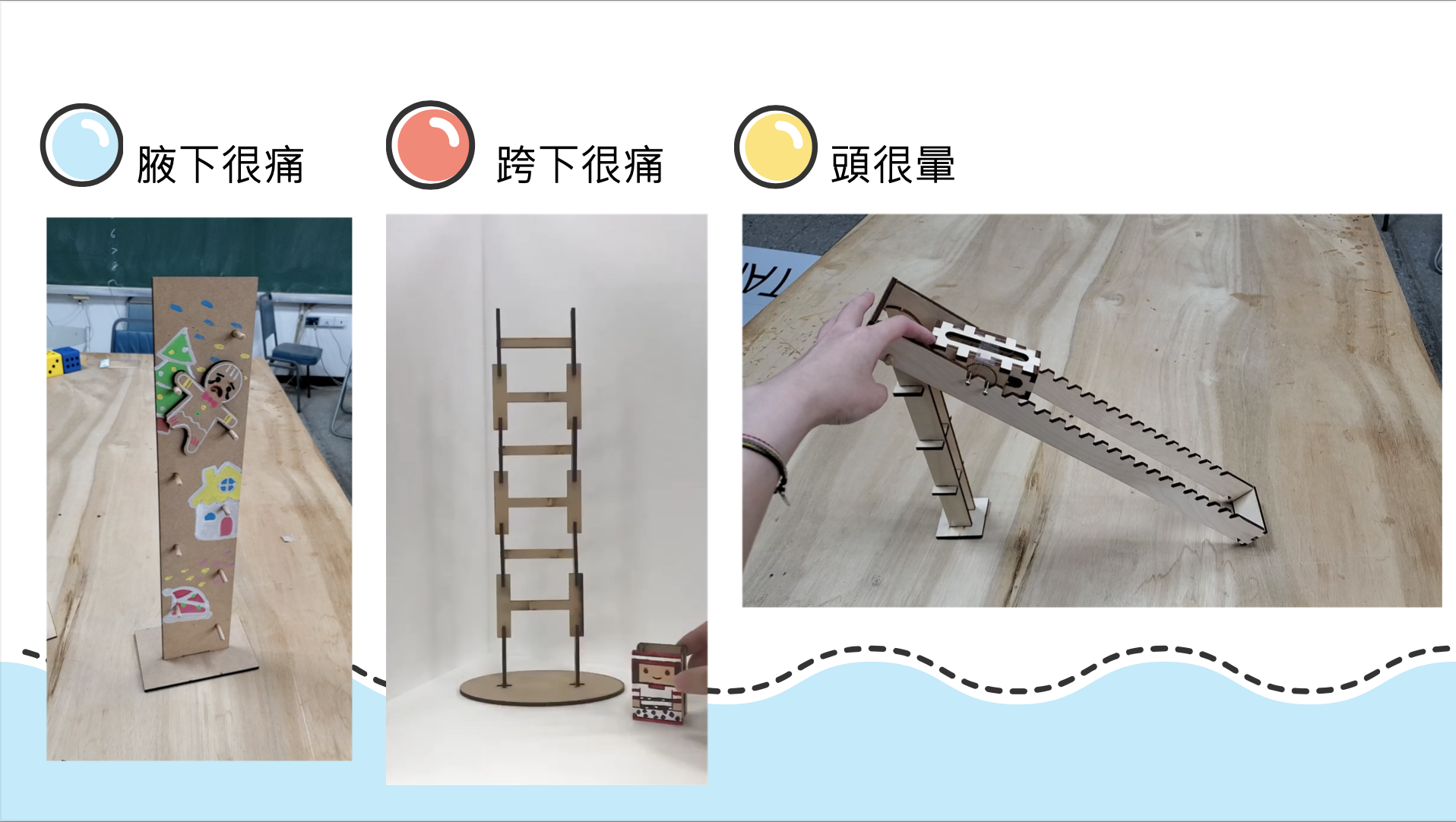
(4) Finished product display
The core value of STEAM education lies in practical inquiry and design innovation, emphasizing the connection with the real world, starting from life and applying it to life (Zhang Yushan, 2019; 2020). This article integrates cross-field aesthetics into STEAM education and designs practical activities for flipping wooden dolls. Teachers can complete it successfully and actively participate in the whole process. Since this course is designed for primary school students, the technical aspect is quite easy for primary school teachers. During the activity, teachers must be reminded at any time that they should think about teaching design issues so that they can immediately bring this activity into the classroom. . Regarding the results of this study, if more discussions on instructional design can be added, it may be of greater help to promote teacher studies in cross-field aesthetic education. This is also an area that can be strengthened in the future when conducting cross-cultural and aesthetic teacher training.